728x90
반응형
Setup
필요한 라이브러리를 import하자.
# To support both python 2 and python 3
from __future__ import division, print_function, unicode_literals
# Common imports
import numpy as np
import os
# to make this notebook's output stable across runs
np.random.seed(42)
# To plot pretty figures
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
mpl.rc('axes', labelsize=14)
mpl.rc('xtick', labelsize=12)
mpl.rc('ytick', labelsize=12)from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.30, random_state=42)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_boundary(clf, X, y, axes=[-1.5, 2.5, -1, 1.5], alpha=0.5, contour=True):
x1s = np.linspace(axes[0], axes[1], 100)
x2s = np.linspace(axes[2], axes[3], 100)
x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(x1s, x2s)
X_new = np.c_[x1.ravel(), x2.ravel()]
y_pred = clf.predict(X_new).reshape(x1.shape)
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#fafab0','#9898ff','#a0faa0'])
plt.contourf(x1, x2, y_pred, alpha=0.3, cmap=custom_cmap)
if contour:
custom_cmap2 = ListedColormap(['#7d7d58','#4c4c7f','#507d50'])
plt.contour(x1, x2, y_pred, cmap=custom_cmap2, alpha=0.8)
plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==0], X[:, 1][y==0], "yo", alpha=alpha)
plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==1], X[:, 1][y==1], "bs", alpha=alpha)
plt.axis(axes)
plt.xlabel(r"$x_1$", fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel(r"$x_2$", fontsize=18, rotation=0)from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_scoreAdaBoost
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
ada_clf = AdaBoostClassifier(
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1), n_estimators=200,
algorithm="SAMME.R", learning_rate=0.5, random_state=42
)
ada_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
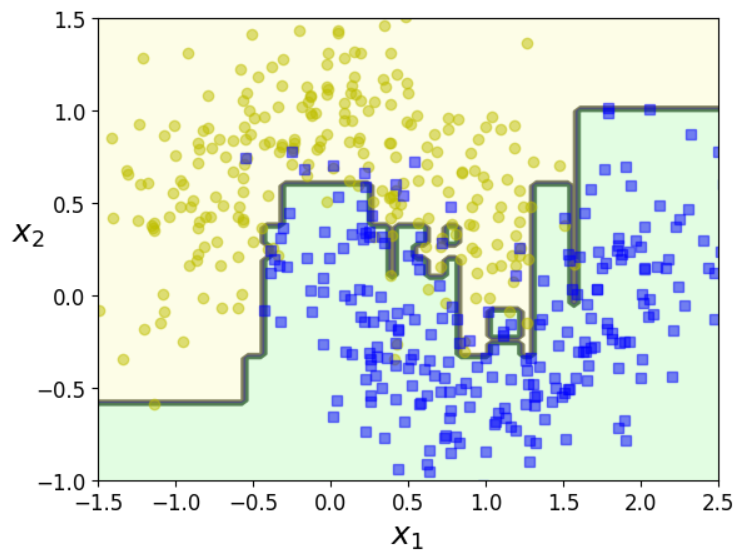
plot_decision_boundary(ada_clf, X, y)- 첫번째 인자는 estimator이다. AdaBoostClassifier는 default로 DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1)이다.
- n_estimator: estimator의 최댓값. best fit이 되면 미리 지정한 숫자 이하에서 멈춘다.
- algorithm="SAMME.R": "SAMME"를 사용하면 discrete boosting algorithm을 적용한다. 일반적으로 "SAMME.R"이 더 빨리 수렴하고 적은 boosting iteration으로도 낮은 test error를 갖는다.
AdaBoost에서 자주 사용하는 메소드는 다음과 같다.
list(m for m in dir(ada_clf) if not m.startswith("_") and m.endswith("_"))
'''
['base_estimator_',
'classes_',
'estimator_',
'estimator_errors_',
'estimator_weights_',
'estimators_',
'feature_importances_',
'n_classes_',
'n_features_in_']
'''반응형
Consecutive Predictors
Support Vector Classifier의 kernel, C, gamma, random_state는 동일하게 하고, sample_weight만 update하여 학습해보자. (Boosting 알고리즘 적용)
sequential learning은 마치 gradient descent과 유사하게 동작하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Note: Sequential Learning은 Parallel이나 Partial하게 학습하지 못한다.
from sklearn.svm import SVC
m = len(X_train)
plt.figure(figsize=(11, 4))
for subplot, learning_rate in ((121, 1), (122, 0.5)):
sample_weights = np.ones(m)
plt.subplot(subplot)
for i in range(5):
svm_clf = SVC(kernel="rbf", C=0.05, gamma="auto", random_state=42)
svm_clf.fit(X_train, y_train, sample_weight=sample_weights)
y_pred = svm_clf.predict(X_train)
sample_weights[y_pred != y_train] *= (1 + learning_rate)
plot_decision_boundary(svm_clf, X, y, alpha=0.2)
plt.title("learning_rate = {}".format(learning_rate), fontsize=16)
if subplot == 121:
plt.text(-0.7, -0.65, "1", fontsize=14)
plt.text(-0.6, -0.10, "2", fontsize=14)
plt.text(-0.5, 0.10, "3", fontsize=14)
plt.text(-0.4, 0.55, "4", fontsize=14)
plt.text(-0.3, 0.90, "5", fontsize=14)
plt.show()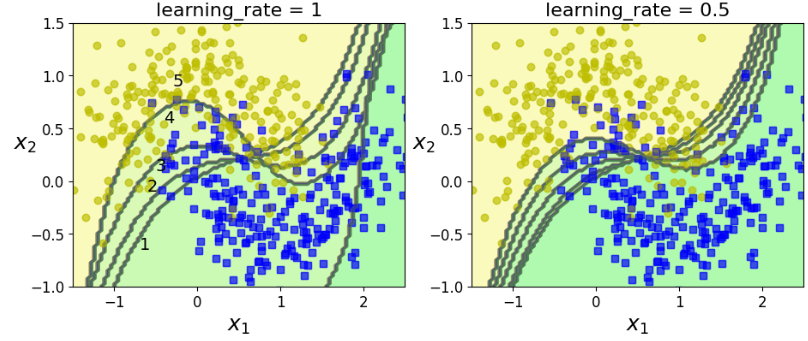
728x90
반응형
'스터디 > 인공지능, 딥러닝, 머신러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Clustering] Partitioning Methods, K-Means Clustering, PAM, k-Medoids Clustering (0) | 2023.05.18 |
|---|---|
| [Clustering] Overview, Approach, Cluster Analysis (0) | 2023.05.17 |
| [Ensemble] AdaBoost (0) | 2023.05.16 |
| [Ensemble] Random Forests in Python (scikit-learn) (0) | 2023.05.13 |
| [Ensemble] Random Forests (0) | 2023.05.12 |



